PPGAN: Privacy-preserving Generative Adversarial Network (under review)
Published in The 25th IEEE International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS) (CCF-C, Core-B Conference), 2019
Abstart
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and its variants serve as a perfect representation of the data generation model, providing researchers with a large amount of highquality generated data. They illustrate a promising direction for research with limited data availability. When GAN learns the semantic-rich data distribution from a dataset, the density of the generated distribution tends to concentrate on the training data. Due to the gradient parameters of the deep neural network contain the data distribution of the training samples, they can easily remember the training samples. When GAN is applied to private or sensitive data, for instance, patient medical records, as private information may be leakage. To address this issue, we propose a Privacy-preserving Generative Adversarial Network (PPGAN) model, in which we achieve differential privacy in GANs by adding well-designed noise to the gradient during the model learning procedure. Besides, we introduced the Moments Accountant strategy in the PPGAN training process to improve the stability and compatibility of the model by controlling privacy loss. We also give a mathematical proof of the differential privacy discriminator. Through extensive case studies of the benchmark datasets, we demonstrate that PPGAN can generate high-quality synthetic data while retaining the required data available under a reasonable privacy budget.
Introduction
training data to perform data mining tasks, in the field of medical and health informatics, such as disease prediction and auxiliary diagnosis. Deep learning models are employed to remember the characteristics of a large number of training sample for classification or prediction purposes. However, organizations such as hospitals and research institutes are paying more and more attention to the protection of data. Additionally, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) issued by the European Union prohibits organizations from sharing private data. It is increasingly difficult for researchers to obtain training data unlimited legally.
Model
As shown in Fig. 3. DPDM reduces the sensitivity of these gradient-decreasing updates (and thus the overall accuracy) by clipping the stochastic gradients, essentially ensuring that the gradient will be within a bounded range. Hence, we only need to add noise proportional to the sensitivity to ensure differential privacy. (In the Algorithm 2.) We present the steps of PPGAN in Fig. 2:
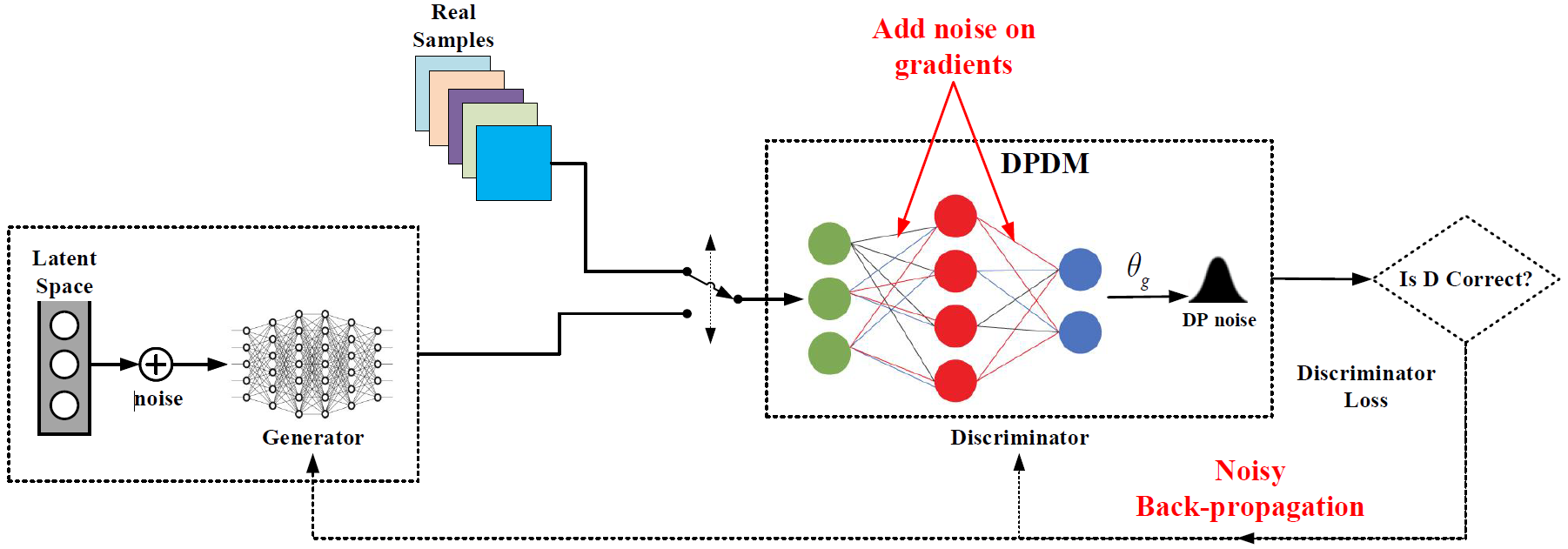
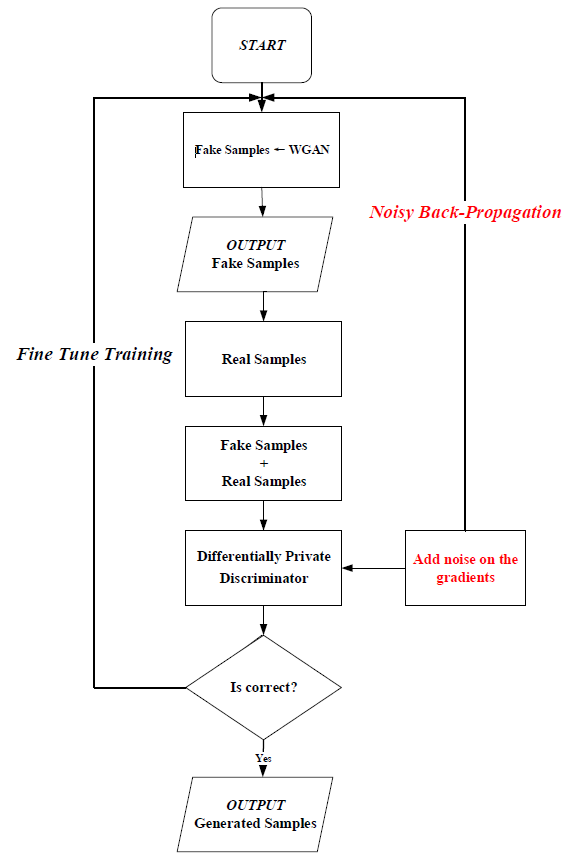
Methods
- Privacy-preserving Generative Adversarial Network (PPGAN)
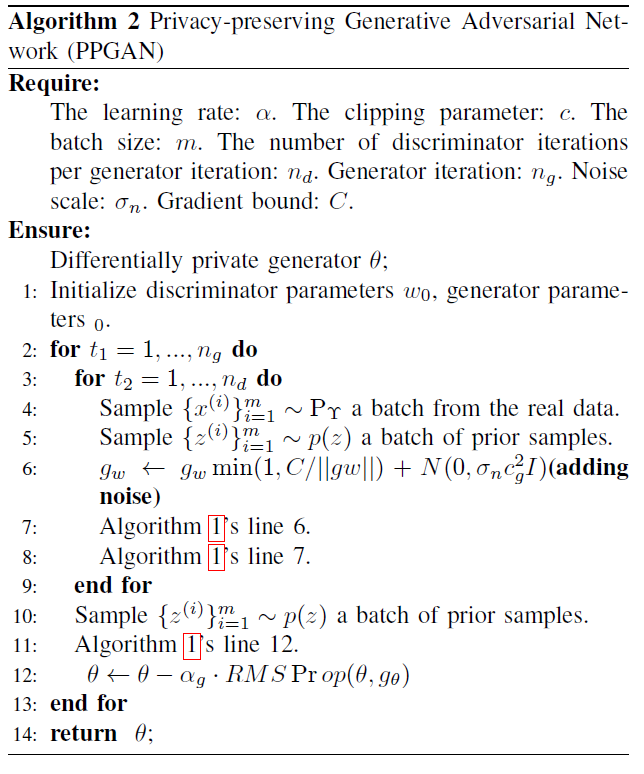
Result
- Relationship between Privacy budget and Generation Performance
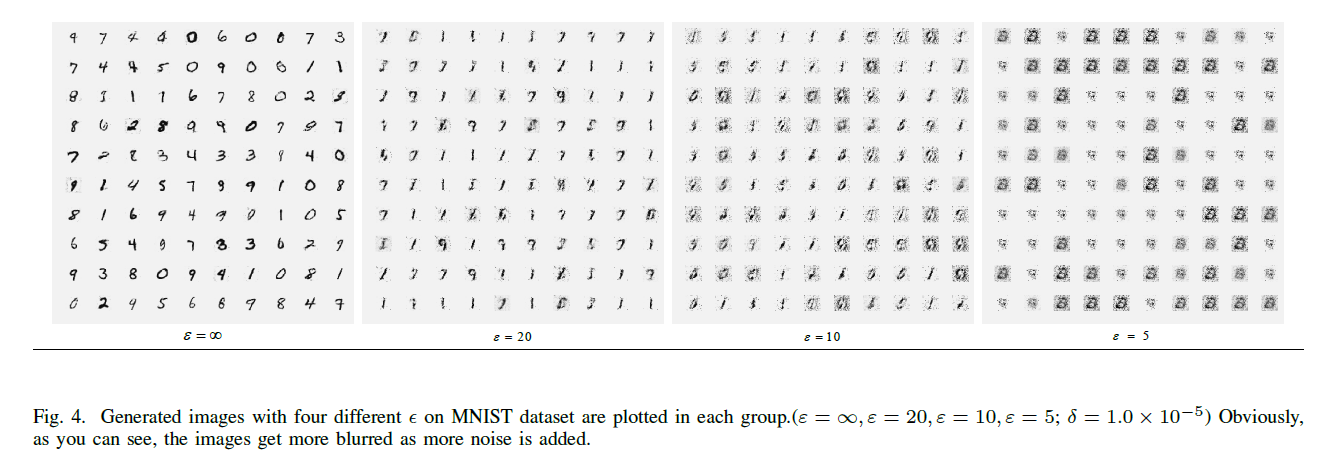
As shown in Fig. 4, as the privacy budget increases, the quality of the generated images is getting worse.
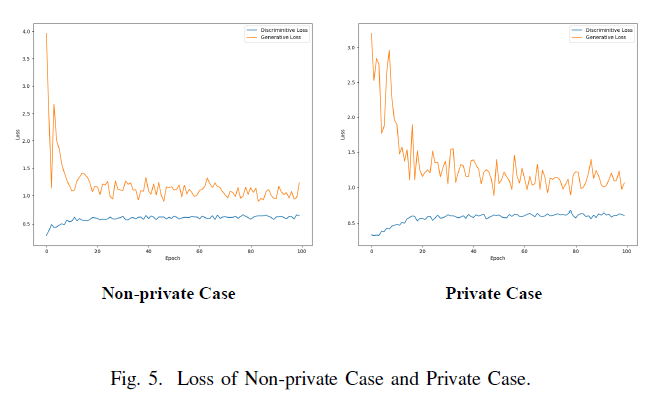
Next, we will focus on the impact of noise on PPGAN’s loss function during training. The result is shown in Fig. 5 In the non-private case, we observe the training loss of the first 100 epoch in training. The result indicates that the loss of GAN is smooth and stable, and no large fluctuations exist in this round of training. When the loss of the PPGAN with noise starts to fluctuate at the tail of the curve, PPGAN can still converge.
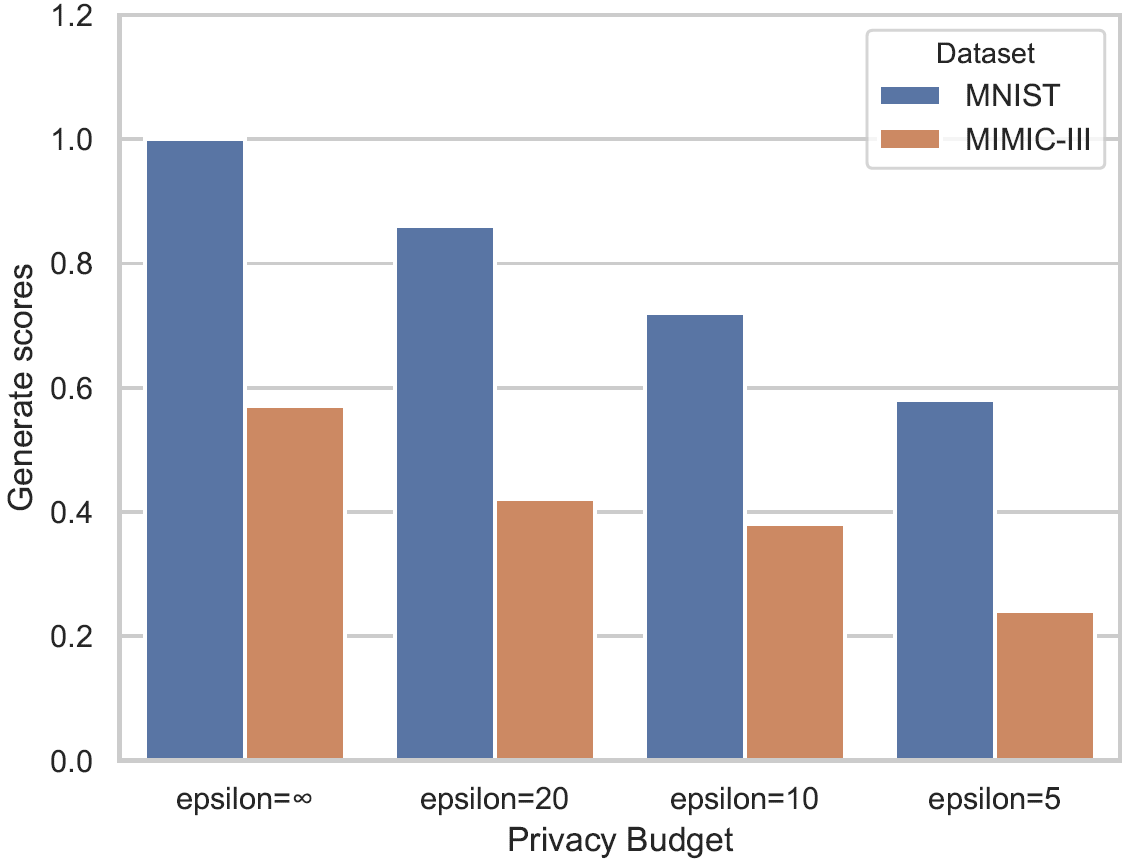
- Relationship between Privacy budget and High-quality Datesets
The generated data’s (generated by PPGAN) generate score is compared to the real data of the MNIST dataset with different privacy budgets. The larger the score value, the better the quality of the data generated by the generator. The figure shows the distribution of the generate scores of PPGAN in the case of = 20; 10; 5.
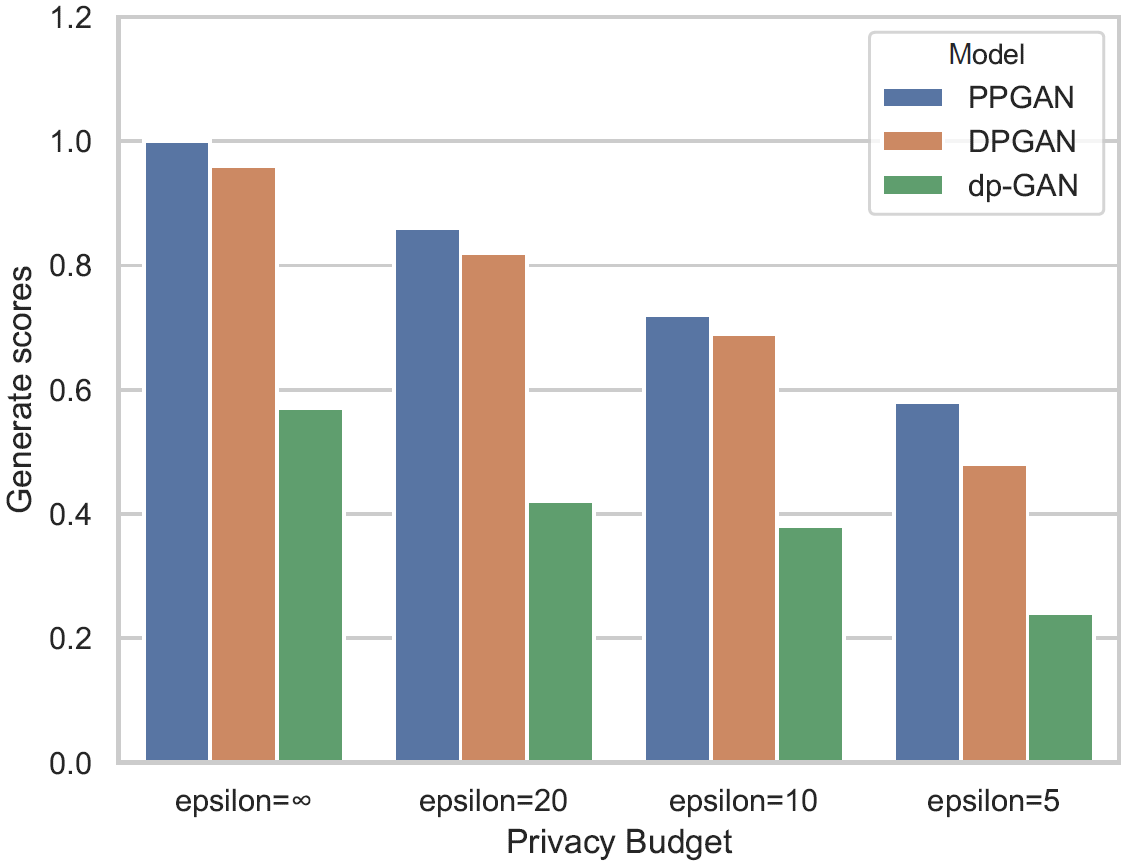
To evaluate the performance of PPGAN, we conpare three solutions, namely dp-GAN, DPGAN and WGAN (Non-private Case) in terms of the quality of the generated data.
Inception scores:
Generate scores:
- Utility Evaluation of PPGAN
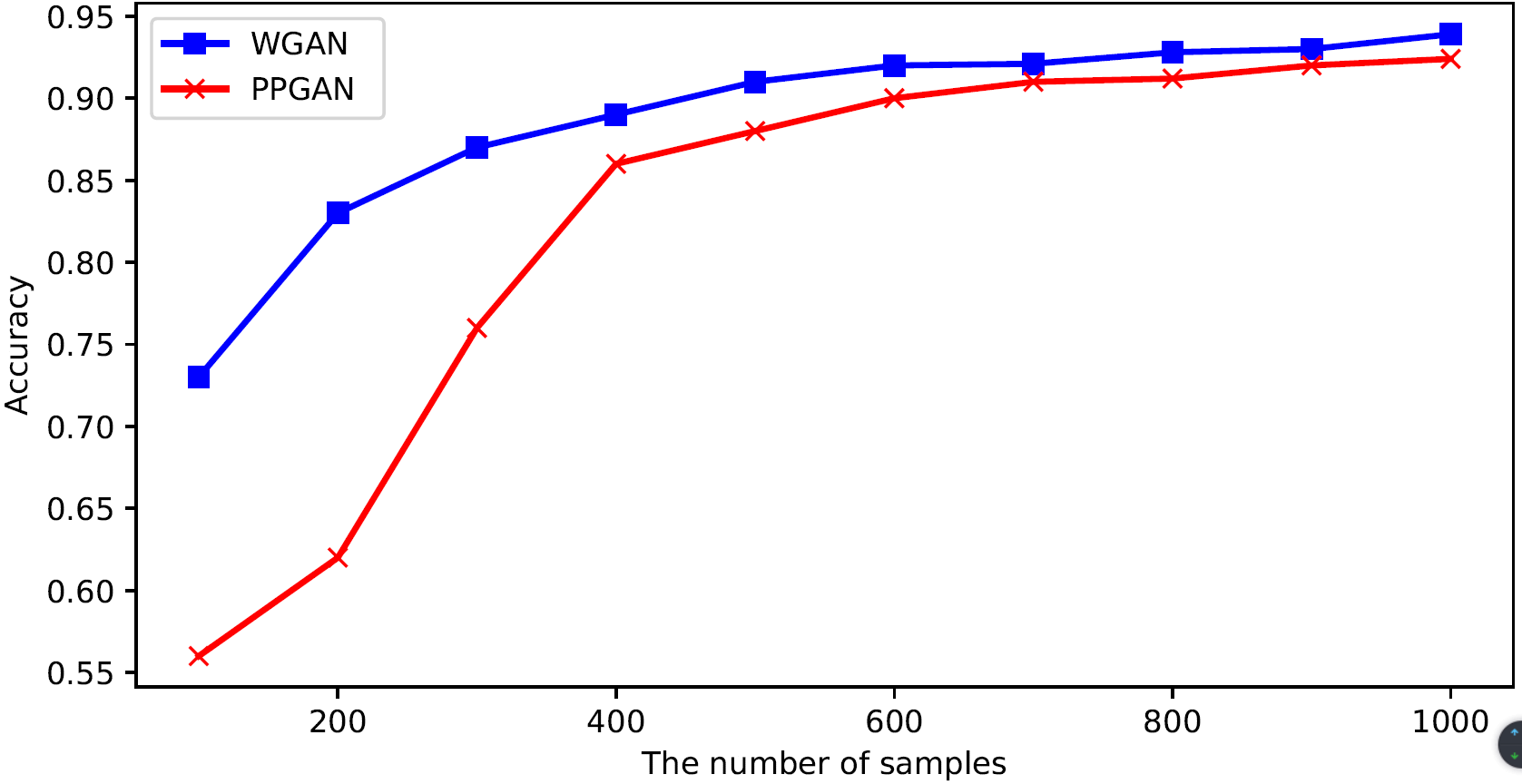
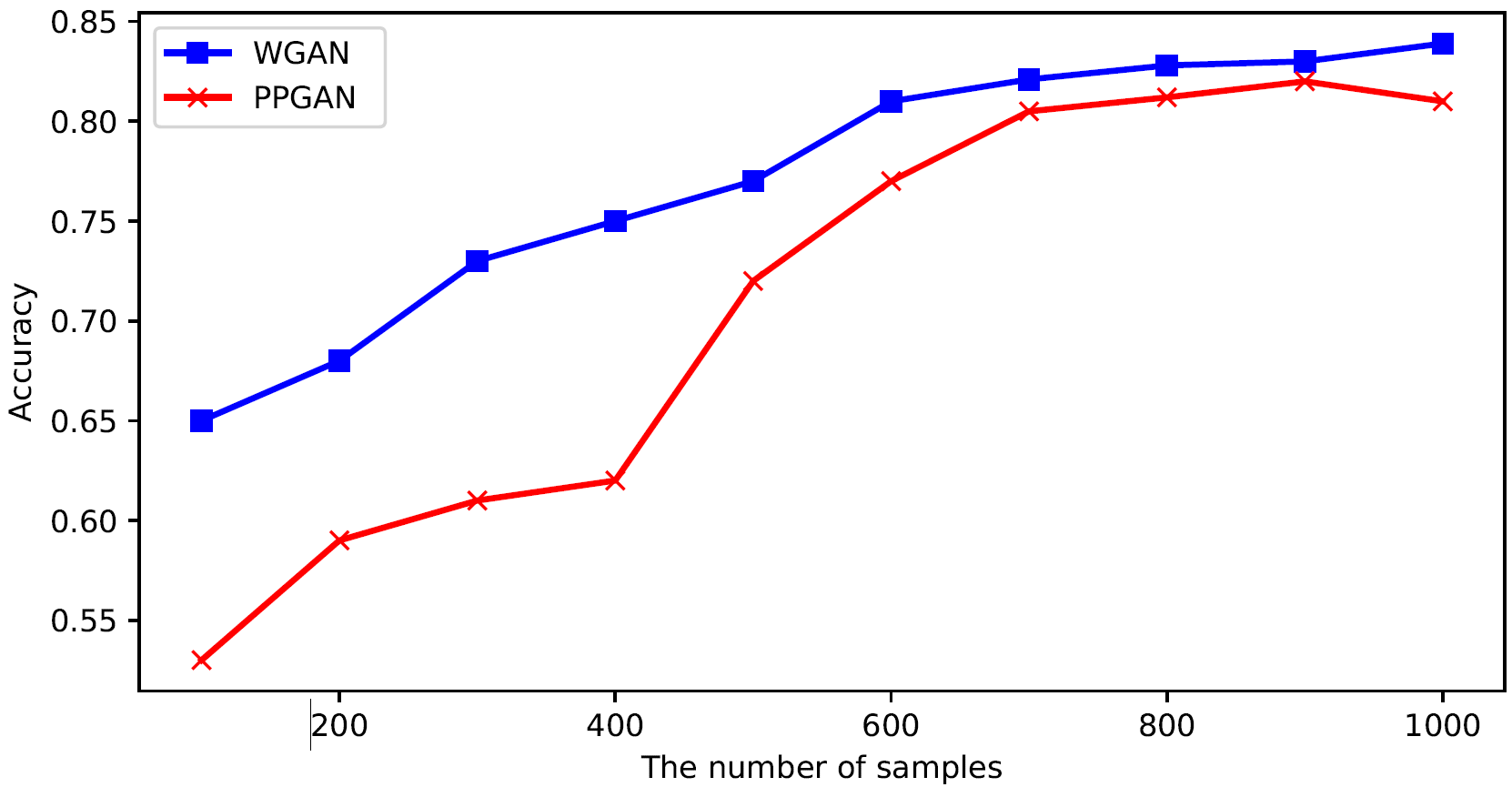
In this subsection, we further compare the performance of PPGAN in specific analytical tasks with the existing model (WGAN) on the MNIST and MIMIC-III datasets.
Conclusion
In this paper, we propose the PPGAN model that preserves the privacy of training data in a differentially private case. PPGAN mitigates information leakage by adding welldesigned noise to the gradient during the learning process. We conducted two experiments to show that the proposed algorithm can converge under the noise and constraints of the training data and generate high-quality data. In addition, our experimental results verify that PPGAN does not suffer from mode collapse or gradient disappearance during training, thus maintaining excellent stability and scalability of model training.
Citations
Coming soon...